[ad_1]

Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
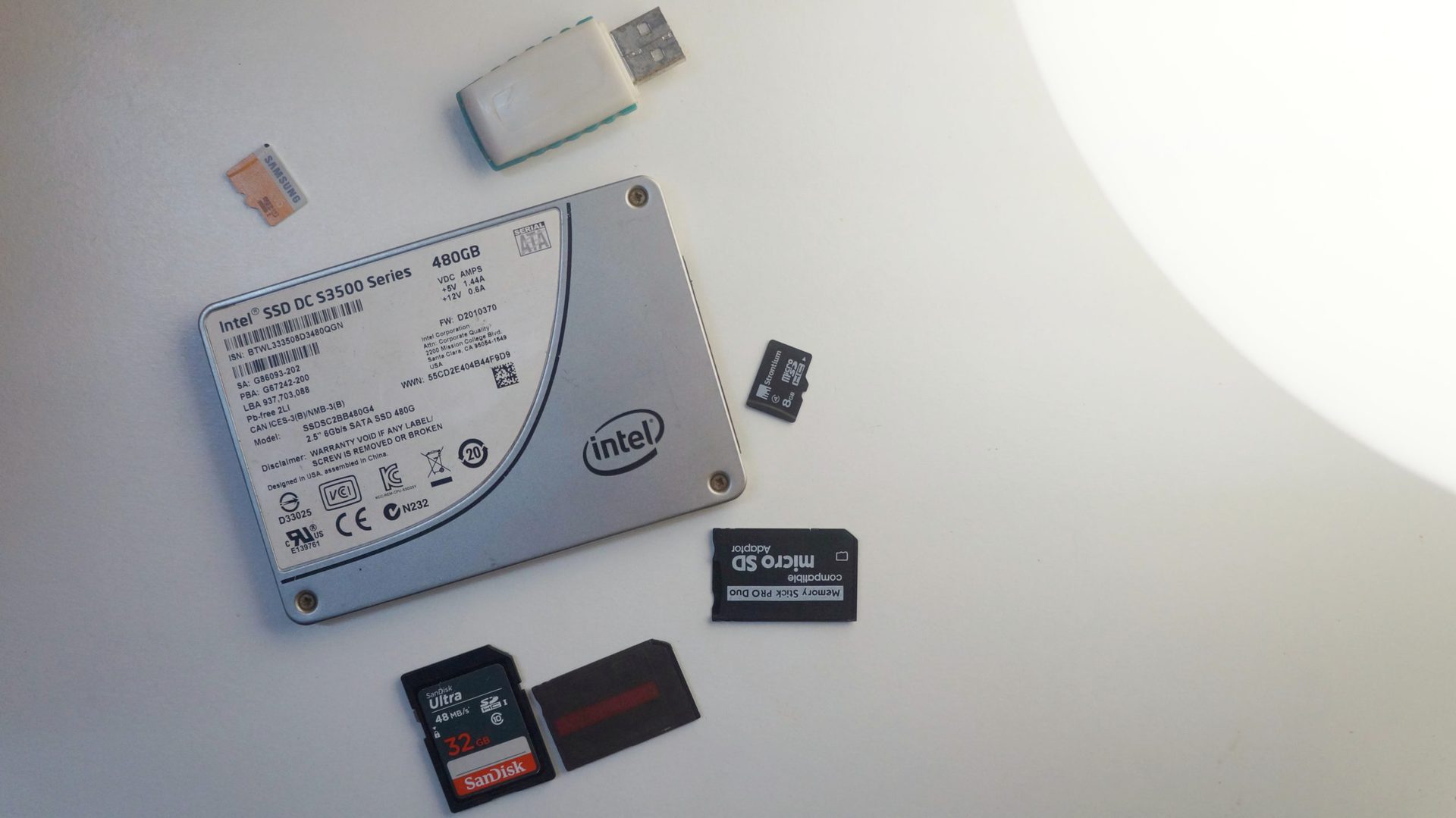
Just about all fashionable gadgets depend on flash reminiscence — an digital information storage know-how that may protect data for lengthy intervals of time. Your smartphone, as an example, makes use of some type of flash reminiscence for storage, and it’s doubtless that the majority laptops and computer systems round you put it to use as effectively. Nonetheless, not all flash reminiscence is created equal — some implementations are far superior to others. So on this article, let’s break down the know-how, the way it works, and the assorted phrases you’ll have heard related to the know-how.
See additionally: One of the best Android telephones with expandable reminiscence
What’s flash reminiscence and why is it so common?

Edgar Cervantes / Android Authority
Flash reminiscence is a sort of non-volatile storage. The non-volatile bit implies that information is retained even when the system fully loses energy. That’s in stark distinction to RAM, a sort of unstable reminiscence that loses all of its information when powered down or reset. Flash reminiscence’s capability to retailer information with out a energy supply, together with different advantages we’ll focus on, makes it preferrred to be used as a storage medium, and it’s solely rising in recognition.
Onerous disks have been as soon as the dominant storage medium for digital gadgets. The primary-generation iPod, as an example, used a 5GB arduous drive from Toshiba. Equally, most laptops and desktop computer systems till the early 2010s had arduous disks as their major storage system. However a lot of the patron electronics business has now dropped arduous disks in favor of flash reminiscence, particularly in purposes like gaming that require a quick storage medium.
Flash reminiscence provides quite a few benefits over arduous drives, together with velocity, sturdiness, and dimension.
Onerous drives have quite a few disadvantages. For one, their spinning platters make them largely mechanical gadgets. In different phrases, they’ve a number of failure-prone shifting elements. Secondly, they’re not very quick, since a magnetic needle has to bodily attain particular elements of a spinning platter to learn and write information.
Flash reminiscence, then again, is solely digital. Knowledge continues to be saved digitally, within the type of 1s and 0s. As a substitute of utilizing magnetism like in arduous drives, nonetheless, flash makes use of so-called reminiscence cells constructed from transistor gates. The absence of shifting elements affords flash memory-based storage gadgets a number of advantages. They usually have longer lifespans, occupy much less house, and function considerably quicker than arduous drives. In fact, the know-how has just a few drawbacks, however moreover value, most don’t actually have an effect on the standard person.
Learn on: One of the best USB flash drives
Flash-related phrases it is best to know

Sarah Chaney / Android Authority
SATA: Launched within the early 2000s, SATA refers back to the communication interface between a pc’s motherboard and storage gadgets like arduous disks. The newest hottest revision, SATA III, provides a most throughput of 600MB/s — removed from the cutting-edge. The usual hasn’t seen any updates since 2009 however stays broadly used at the moment.
NVMe: NVMe or non-volatile reminiscence specific is a communication protocol for storage gadgets. Not like SATA, NVMe was designed for larger throughput storage gadgets like SSDs. Since NVMe SSDs have a direct path to the CPU, they’re usually considerably quicker than SATA SSDs. NVMe can hit speeds of three,500MB/s, 6x quicker than SATA III.
PCIe: PCIe stands for peripheral element interconnect specific and offers the communication spine for NVMe gadgets. The efficiency of an NVMe drive could differ relying on the CPU’s PCIe capabilities. For instance, a PCIe Gen 4 NVMe SSD could exhibit slower speeds in older computer systems with solely Gen 3 capabilities. Then again, newer gadgets just like the PlayStation 5 mandate PCIe Gen 4 NVMe SSDs above a sure velocity threshold for a constant person expertise.
M.2: M.2 refers to a bodily connector used for growth playing cards. The slot is usually discovered on pc and laptop computer motherboards, however you may additionally see it on different gadgets just like the PlayStation 5 (the inexperienced house pictured above). An M.2 connector might be electrically wired as much as perform in both SATA or PCIe mode. Laptops usually use M.2 for high-bandwidth growth playing cards like Wi-Fi playing cards and SSDs.
How is the know-how associated to SSDs, UFS, and eMMC?
Storage gadgets that make the most of flash reminiscence are available in numerous styles and sizes, relying on their supposed use case. A pc’s major boot drive, for instance, must be quicker and extra sturdy than a thumb drive that you simply’ll solely use to retailer media information. SSDs, eMMC chips, and SD playing cards all use flash reminiscence, however precise implementations can differ.
Strong State Drives (SSDs) sometimes comprise extra than simply flash reminiscence — many additionally home a DRAM cache and reminiscence controller. The previous can velocity up reads and writes, however finances drives have a tendency to not embody it. The controller, in the meantime, helps the system interface with the drive’s saved information. In some instances, it could possibly additionally assist enhance the drive’s longevity by strategies resembling put on leveling and error correction.
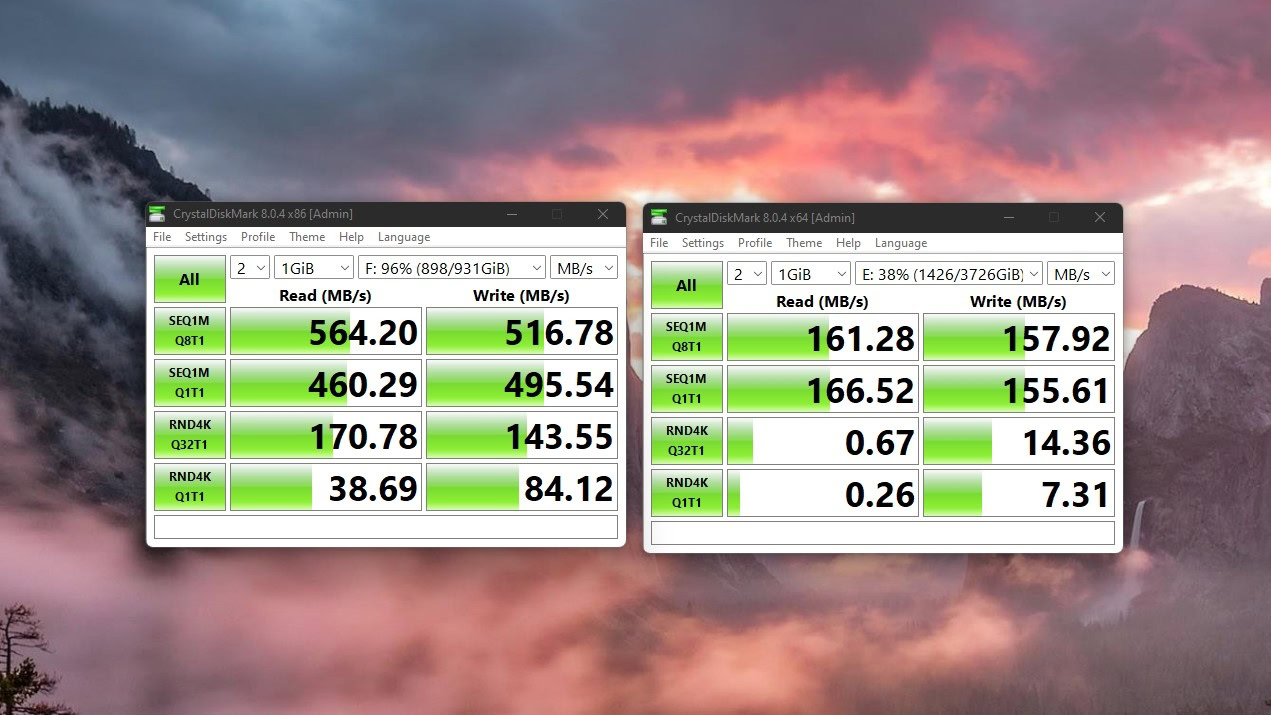
Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
SSDs (left) take pleasure in quicker learn and write speeds than arduous drives (proper)
SD playing cards and USB drives are a lot easier, by comparability. Each occupy a a lot smaller footprint than SSDs and, consequently, are additionally fairly a bit slower. Moreover, SSDs sometimes home a number of reminiscence packages to extend the entire capability. Smaller SD playing cards and USB drives can’t achieve this since they need to squeeze right into a smaller kind issue.
SD playing cards sometimes supply worse sturdiness and speeds than SSDs, though each share the identical underlying know-how.
Lastly, you’ll have additionally heard of eMMC and UFS flash storage chips within the context of smartphones, tablets, and laptops. MMC stands for embedded MultiMediaCard, whereas UFS is brief for Common Flash Storage. You’ll discover these embedded chips soldered straight onto a tool’s motherboard.
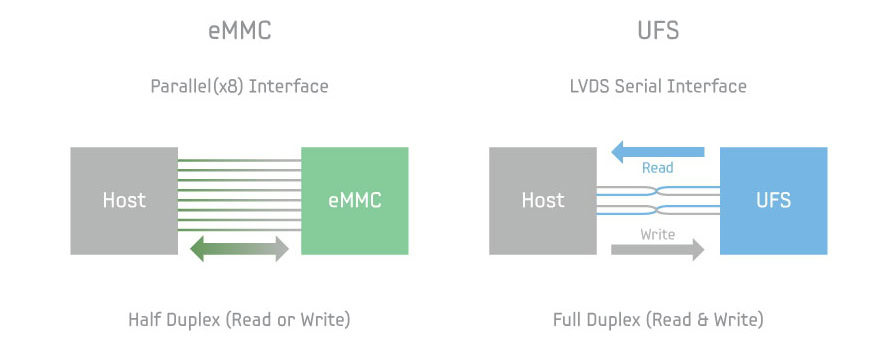
Today, UFS has began to exchange eMMC as the usual for smartphone storage. The previous is considerably quicker (as much as 2,100 MB/s vs 250MB/s) because it helps simultaneous learn and write — consider UFS as a two-way multi-lane freeway and eMMC as a one-way highway. Each are nonetheless considerably quicker than arduous drives, although.
Storage speeds are extra vital for sure purposes than others. Excessive-resolution video recording, as an example, can overwhelm most lower-end SD playing cards. Equally, video games and different intensive workloads can profit from quicker storage.
With out getting too deep into the specifics of the electronics concerned, flash reminiscence shops information in reminiscence cells. These cells comprise floating-gate transistors that may lure electrons for a protracted time frame, however not ceaselessly. These cells have three operations: learn, write, and erase, relying on the place you apply a voltage. To carry out a write operation, the floating gate within the reminiscence cell is both charged or discharged — the previous denotes a logical 0, whereas a discharged state signifies 1.
Fashionable storage gadgets set up reminiscence cells in pages that permit massive quantities of information to be accessed concurrently as an alternative of cell-by-cell. The commonest kind of flash storage, referred to as NAND flash, comprises blocks of 32 or 64 pages.
A client system containing NAND flash, like a USB drive or SSD, has hundreds of thousands of reminiscence cells stacked horizontally, vertically, or in each dimensions — the latter is usually referred to as 3D NAND. As you’d count on, a tool that requires such exact operations and density is costlier to fabricate than conventional arduous drives.
NAND flash’s complexity implies that it’s costly to fabricate.
Producers have provide you with methods to fight flash reminiscence’s excessive value, although, with the most typical method being the usage of multi-level cells. As a substitute of storing a single 0 or 1, triple-level cells (TLC) and multi-level cells (MLC) can retailer two, three, or extra bits. Whereas this technique improves storage density and reduces manufacturing prices, it additionally has a detrimental impact on velocity and sturdiness. Nonetheless, the cost-benefit implies that most consumer-grade storage gadgets at the moment use TLC or MLC-based flash reminiscence as an alternative of single-level cells (SLC).
See additionally: One of the best inside and exterior SSDs
What are the know-how’s limitations?

Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
Flash storage has develop into the usual for compact digital gadgets nowadays, however the know-how is way from excellent. Apart from excessive costs, which we’ve already mentioned, flash reminiscence can undergo information degradation or bit rot over time. If saved in an unpowered state for a number of years, reminiscence cells can undergo from electron leakage and, ultimately, information loss. Whereas arduous drives can even undergo from bit rot, they sometimes final a bit longer when powered down.
A much bigger difficulty with flash storage is write endurance, or program/erase cycles. In a nutshell, it refers back to the quantity of information you may write earlier than the reminiscence cells ultimately put on out. Typically talking, the extra data you squeeze per reminiscence cell (TLC and MLC-type drives), the more serious the endurance.
Flash storage suffers from restricted endurance — it could possibly solely survive a restricted variety of rewrites.
Storage system producers sometimes assure a drive’s lifespan as much as a sure utilization level, quoted in TBW or complete bytes written. The 1TB variant of Samsung’s 860 Evo SSD, as an example, has a quoted endurance of 600TBW. A drive should work past its rated TBW — simply don’t count on any guarantee from the producer. Increased endurance drives sometimes value extra — particularly these designed for enterprise use.
Lastly, flash storage nonetheless can’t beat arduous disks when it comes to capability. Most client SSDs high out at 2-4TB, when you can simply purchase arduous disks that exceed 10 and even 15TB on the similar value level. This may occasionally change in some unspecified time in the future sooner or later, however for now, arduous disks reign supreme for archiving massive quantities of information.
Proceed studying: A newbie’s information to NAS drives
[ad_2]
Source link



