Robert Triggs / Android Authority
Sony is at all times on the slicing fringe of cell digital camera expertise, and a latest report in Nikkei Japan signifies that the corporate believes its breakthroughs will see smartphones match and even overtake the capabilities of DSLR and mirrorless cameras as quickly as 2024.
At a latest enterprise briefing, President and CEO of Sony Semiconductor Options (SSS), Terushi Shimizu, famous that “nonetheless photographs [from smartphones] will exceed the picture high quality of single-lens reflex cameras inside the subsequent few years.” A slide from the identical briefing factors to 2024 because the timeline the place Sony sees that smartphone “nonetheless photographs are anticipated to exceed ILC [interchangeable lens camera] picture high quality.”
These are barely alternative ways of claiming the identical factor: telephones will surpass DSLR and mirrorless digital camera picture high quality within the subsequent two to a few years. In fact, there’s all kinds of mirrorless cameras with capabilities and costs to swimsuit a variety of budgets. Beating the cheaper fashions isn’t as tough as overtaking the premium tier. So is that this simply Sony advertising and marketing fluff or is there reality to this declare?
Learn additionally: The very best digital camera telephones you should purchase
Cell cameras proceed to enhance

Eric Zeman / Android Authority
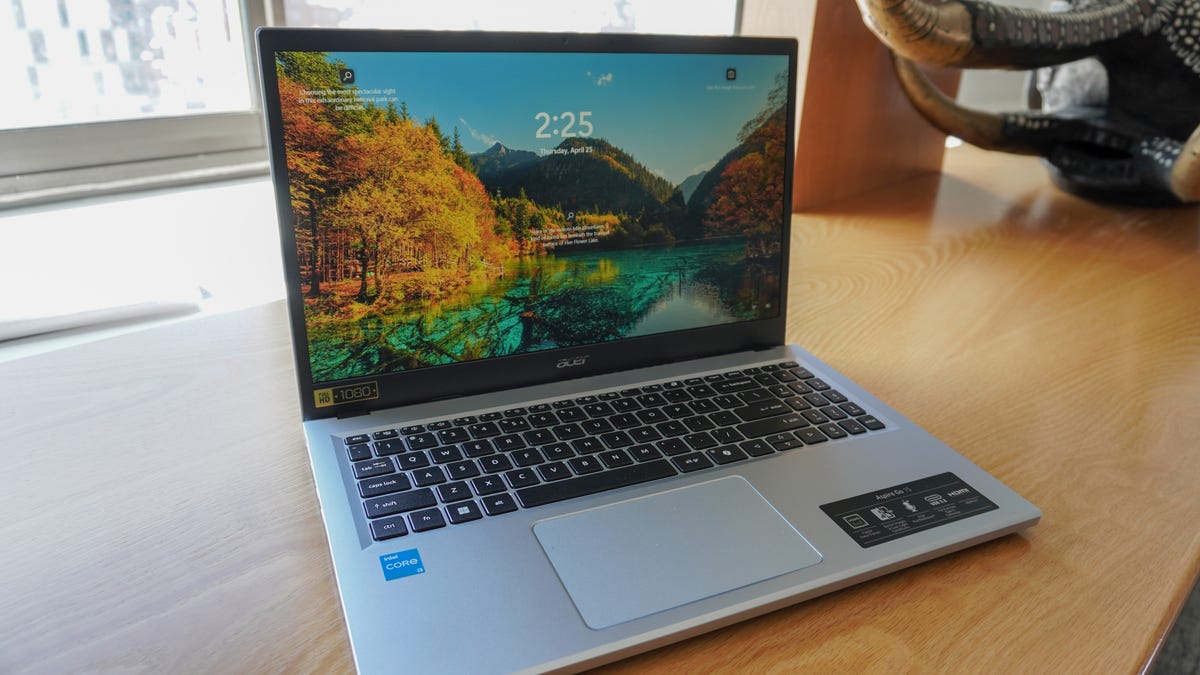
There are a number of key parts Sony cited so as to add confidence to its declare. First, cell picture sensors are anticipated to achieve and doubtlessly exceed one inch in dimension within the subsequent two years. It’s price noting that the Sony Xperia Professional I already boasts a 1-inch 20MP main picture sensor. Nevertheless, resulting from distance constraints between the lens and sensor, Sony’s ultra-premium digital camera solely makes use of 12MP of the sensor’s floor, the equal of a roughly 1/1.3 inch sensor that’s fairly widespread in different flagship smartphones. This can be a downside that Sony doesn’t immediately tackle, and the restrictions of the smartphone type issue will probably preserve a lid on simply how huge cell sensors can change into.
Sony sees new sensors, AI, and high-speed readouts because the keys to overtaking DSLR cameras.
That mentioned, Sony keenly highlighted the potential of its new two-layer CMOS sensor breakthrough. This new setup separates the manufacturing course of for the photodiode and transistor layers, optimizing every extra successfully. Earlier designs have each parts on the identical wafer. Sony states that the brand new construction saturates every pixel with twice as a lot mild, tremendously rising the dynamic vary and lowering noise in low mild when in comparison with typical back-illuminated picture sensors.
Even when smartphone sensors can’t change into sufficiently big to rival APS-C cameras, smaller sensors will be capable to seize rather more mild within the close to future, closing the hole. It’s not but recognized when this expertise will make its option to smartphones, but it surely has appeared in Sony’s top-of-the-line mirrorless cameras.
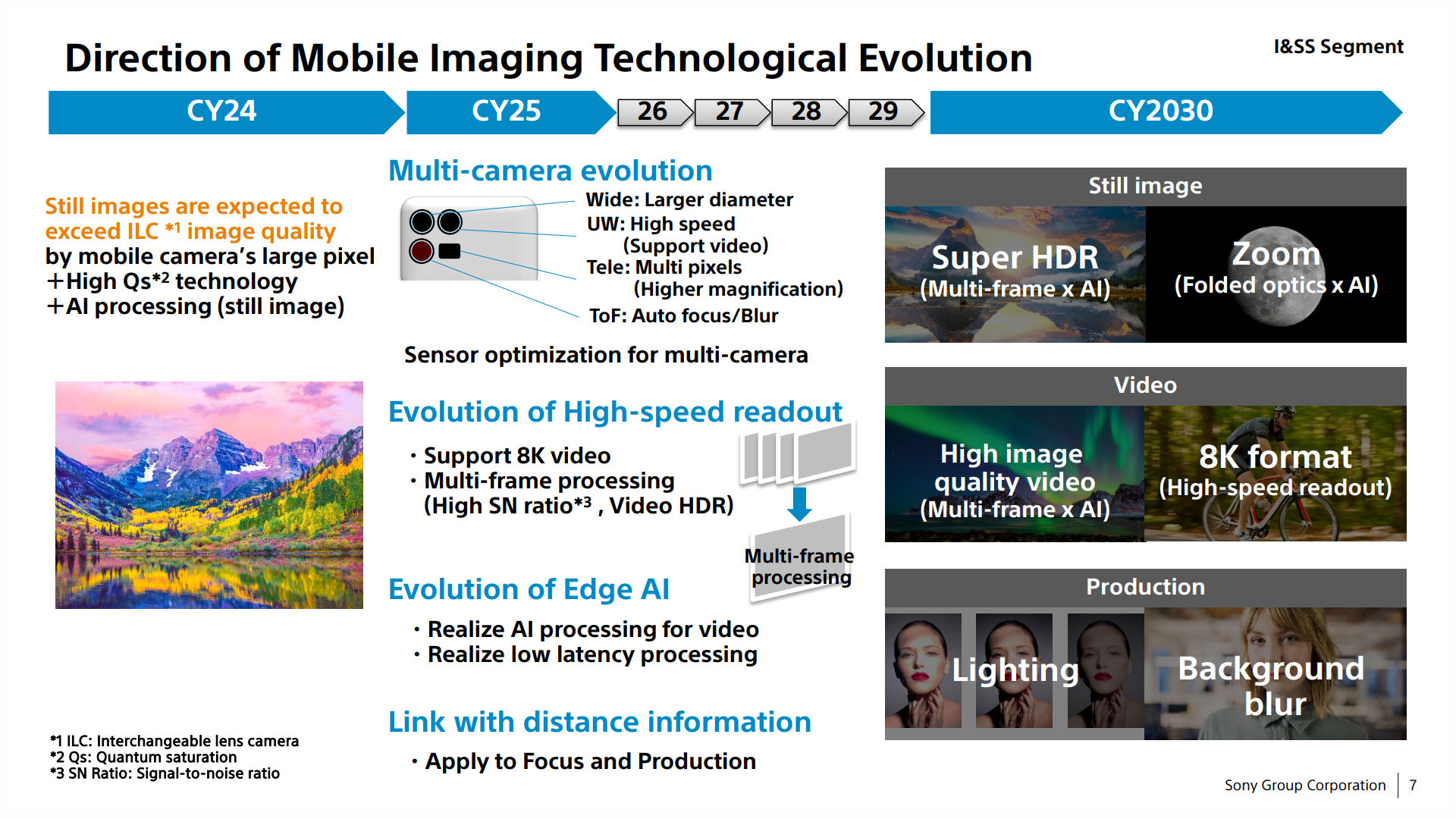
Thirdly, Sony notes the expansion in AI processing capabilities that, when paired with improved {hardware}, proceed to push the boundaries of multi-frame HDR, longer-range zoom, and better high quality video recording. It’s simple that computational images already helps smartphone cameras punch properly above their station. Simply see Google’s $599 Pixel 6, for instance, in addition to the broader development of mixing conventional picture sign processing with machine studying silicon, each on-chip and in-device. Smartphone processing prowess already exceeds DSLR cameras and is more likely to speed up.
Extra: Why customized imaging chips are the following cell images battleground
Along with the presentation, Sony can also be debuting the cell trade’s first variable focal size digital camera within the Xperia 1 IV. Starting from 85-125mm with a single lens, the periscope digital camera gives a DSLR zoom-lens-like expertise in a cell type issue. If it’s doable to broaden the vary of focal lengths, this expertise might negate a few of the points stemming from the usage of a number of picture sensors, from prices and area, to picture and lens high quality inconsistencies. Maybe at some point, telephones will cast off a number of cameras altogether.
Smartphone processing prowess already exceeds DSLR cameras and is more likely to speed up.
Mixed with 8K high-speed readouts, improved depth data and software program blur, and post-processing lighting changes, Sony is betting that it is going to be even tougher to inform the distinction between skilled and smartphone footage in simply two brief years.
Smartphones surpassing DSLR cameras, actually?

Robert Triggs / Android Authority
There’s little doubt that smartphones nonetheless have some option to go earlier than reaching the bounds of the shape issue, however how a lot farther they’ll go and the way shortly is much less clear lower. Yearly enhancements have been slowing in lots of regards, with incremental enhancements to picture high quality tougher to come back by every technology. However that’s extra of a testomony to how good smartphone images has come in recent times. In good lighting and more and more in low mild, it’s usually laborious to fault high-end smartphone cameras.
Nevertheless, as we talked about, it’s tough to suit bigger picture sensors into telephones with out considerably rising the dimensions of digital camera bumps and/or cellphone thickness. This is without doubt one of the explanation why periscope cameras exist, rising the gap between the lens and sensor for an extended focal size with no cumbersome cellphone. The trade-off is the area required, plus the sensor needs to be small to slot in the physique at 90 levels and due to this fact captures much less mild. Even when higher sensors come alongside, how a lot room can telephones sacrifice to the digital camera array somewhat than battery, haptics, audio system, and different parts?
See additionally: Why are smartphone digital camera bumps changing into so enormous?
Though we may be approaching the 1-inch main sensor, ultrawide and telephoto sensors are nonetheless tiny by comparability (usually nonetheless 1/2.5″ or under). It’s uncertain we’ll see a digital camera array with three massive, high-quality sensors any time quickly, however we’ve seen fashions dabble with two bigger sensors. Telephones could also be caught with various ranges of picture high quality from their main, ultrawide, and zoom lenses, significantly in low mild and HDR environments. One thing that DSLR and mirrorless cameras don’t have to fret about (lens high quality is the issue there).
Physics places a restrict on the dimensions and high quality of cell picture sensors and lenses.
The opposite half of the smartphone digital camera “high quality” downside is lenses and aperture. Barring just a few switchable aperture telephones, handset cameras are caught with mounted apertures and are due to this fact restricted by ISO noise and shutter velocity to steadiness their publicity. Whereas that is fantastic in some situations, it’s a difficulty for superior photographers who demand whole management. Notably for portraits and macro pictures that demand a large aperture for comfortable bokeh.
Excessive-quality but tiny lens parts which are free from distortion whereas nonetheless offering a large aperture are very difficult and costly to construct. Although smartphones boast seemingly broad apertures and focal lengths equal to common full-frame digital camera lenses, they’re removed from the actual deal by way of producing the distortion-free edges and creamy bokeh each photographer wishes. Take a look at the examples under shot with the Samsung Galaxy S22 Extremely’s 22mm main and 70mm telephoto versus a roughly equal mirrorless with 25mm and 80mm lenses.
Whereas the 22mm lens footage are close-ish, it’s price noting that the mirrorless is working with a small f/3.5 aperture versus the S22 Extremely’s f/1.9, but it nonetheless achieves much less noise and richer bokeh. Why? As a result of the Extremely’s sensor is near the lens and depends on a crop to create the equal focal size on the expense of depth of discipline. In different phrases, the S22 Extremely, and different telephones, depend on shut topics to supply bokeh somewhat than aperture and focal size. The telephoto comparability highlights this extra clearly. The mirrorless achieves a far shallower depth of discipline regardless of carefully matching the Extremely’s f/2.4 aperture lens and focal size.
See additionally: These images suggestions will enable you to take your pictures to the following stage
Regardless of claims of comparable apertures and focal lengths, smartphones depend on crops to fiddle the numbers, that means you possibly can’t receive the identical depth of discipline as an ASP-C or full-frame digital camera. You’ll obtain an analogous bokeh with a DSLR lens aperture nearer to f/5 for the 2mm main and f/12 for the 70mm telephoto. Not what you need for portrait images, therefore telephones’ reliance on software program portrait modes and synthetic blur.
There are nonetheless footage you merely cannot seize with one of the best smartphone.
Nevertheless, even one of the best portrait mode software program blurs can’t make up for the look of this pure bokeh. In fact, this hole might shut within the subsequent two years, however a variety of smartphone images fundamentals must enhance, together with the algorithms.
Closing ideas

Robert Triggs / Android Authority
The very best smartphones have already decimated the point-and-shoot digital camera and are actually closing in on the decrease echelons of the DSLR/mirrorless digital camera markets. Advances in sensor {hardware} and variable zoom lenses are closing the {hardware} hole, whereas AI processing energy, portrait images enhancements, and auto HDR strategies already usually exceed what you’ll discover in lots of DSLRs.
Sony’s expectation that smartphones will surpass the picture high quality of interchangeable lens cameras in 2024 is more likely to be correct, albeit with many caveats. It’s actually doable within the technical sense of noise and lightweight seize, however much less clear lower by way of flexibility and creative high quality. Even so, we’ve already seen the trade’s route, with bigger sensors, higher lenses, and concepts like software program bokeh and portrait lighting permitting customers to shortly share aggressive pictures in a variety of situations. Extra so with more and more commonplace RAW enhancing instruments too. And the one method is up, significantly the place AI and video are involved.
Telephones are closing the hole with improved mild seize, HDR, and AI processing however DSLR is more likely to stay extra artistically versatile.
That mentioned, ultrawide and zoom digital camera capabilities are much less constant as we speak, and these extremes are tougher to compensate for with good software program. It could take longer than a few years for smartphones to be as versatile as a high quality mirrorless digital camera setup. To not point out overcoming the shape issue’s limitations with mounted apertures, restricted depth of discipline, and a number of picture sensors.
Up subsequent: How Vivo and Zeiss are constructing smartphone cameras for the TikTok technology
Adventurous {and professional} photographers actually received’t be ditching their professional-grade gear for a cellphone digital camera within the subsequent couple of years. There’ll nonetheless be footage you merely can’t seize with smartphone {hardware}, although that hole is narrowing yearly.
Will smartphones surpass mirrorless cameras by 2024?
137 votes












