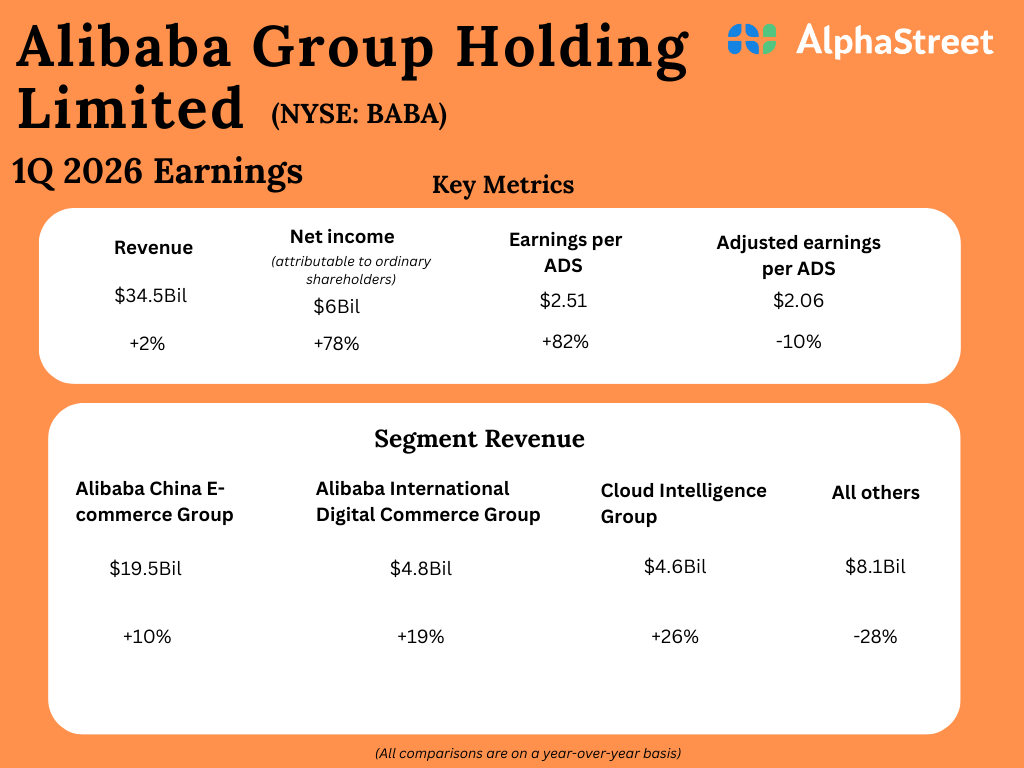
Chinese language tech firm Baidu introduced Monday it might probably promote some robotaxi rides with none human employees within the autos.
Baidu
BEIJING — Chinese language robotaxi corporations are increasing overseas at a quicker clip than U.S. rivals Waymo and Tesla — at a time when trade leaders say autonomous driving is lastly close to an inflection level.
“I feel robotaxi has reached a tipping level, each right here in China and within the U.S.,” Baidu CEO Robin Li stated Tuesday on an earnings name, based on a FactSet transcript.
“There are sufficient individuals who have [had the] likelihood to expertise driverless rides, and the phrase of mouth has created constructive social media suggestions,” he stated, noting that the broader public publicity may velocity up regulatory approval.
His feedback echoed related notes of optimism in the previous few weeks from Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang and Xpeng Co-President Brian Gu — who reversed his beforehand cautious stance after faster-than-anticipated tech advances. Xpeng is launching robotaxis within the southern Chinese language metropolis of Guangzhou subsequent 12 months.
It is a international market with vital development potential, doubtless value greater than $25 billion by 2030, based on Goldman Sachs’ estimates in Could.
To grab that chance, Chinese language corporations are aggressively increasing abroad and declare they’re shut to creating robotaxis a viable enterprise, quite than merely burning money to seize market share.
Within the final 18 months, Baidu, Pony.ai and WeRide landed partnerships with Uber that permit customers of the ride-hailing app to order a robotaxi in particular places, beginning within the Center East.
Such tie-ups “might be vital to success” as they allow robotaxi corporations to function extra effectively and attain profitability extra shortly, stated Counterpoint Senior Analyst Murtuza Ali.
As soon as we will generate revenue for each single automotive in a second-tier metropolis [like Wuhan] in mainland China, we will generate earnings in plenty of cities internationally.
Halton Niu
Common supervisor for Apollo Go’s abroad enterprise
Increasing on expertise at house
Baidu says that since late final 12 months, its Apollo Go robotaxi unit has reached per-vehicle profitability in Wuhan, the place the corporate has operated over 1,000 autos in its largest deployment in China.
Meaning ridership is sufficient to offset a Wuhan taxi fare that is 30% cheaper than in Beijing or Shanghai, and much beneath costs within the U.S. or Europe. Moreover growing autonomous driving techniques, Baidu has additionally produced electrically-powered robotaxi autos — with out counting on a third-party producer — which might be 50% cheaper.
“As soon as we will generate revenue for each single automotive in a second-tier metropolis [like Wuhan] in mainland China, we will generate earnings in plenty of cities internationally,” Halton Niu, basic supervisor for Apollo Go’s abroad enterprise, informed CNBC.
“Scale issues,” he stated. “Should you solely deploy, for instance, 100 to 200 vehicles in a single metropolis, when you solely cowl a small space of town, you’ll be able to by no means turn into worthwhile.”
How U.S. rivals stack up
Scale stays the dividing line. Within the U.S., Alphabet-owned Waymo operates greater than 2,500 autos and is increasing quickly from main cities in California to Texas and Florida, with plans to enter London subsequent 12 months, following its first abroad enterprise in Tokyo.
Tesla sells its electrical vehicles in China, and reportedly confirmed off its Cybercab in Shanghai this month. But it surely started testing its robotaxis in Texas solely in June, and this week obtained a allow to function in Arizona.
Amazon’s Zoox can also be ramping up its growth within the U.S., however has not launched abroad plans.
The three corporations haven’t disclosed plans to interrupt even on their robotaxis.
Baidu Apollo Go’s Niu didn’t rule out an growth into the U.S. However for now, the robotaxi operator plans to enter Europe with trials in elements of Switzerland subsequent month, following their growth within the Center East this 12 months.
Abu Dhabi final week gave Apollo Go a allow to cost fares to the general public for absolutely driverless robotaxi rides, that are operated regionally below the AutoGo model, eight months after native trials started in elements of town.
However Chinese language startup WeRide stated it acquired an identical allow on Oct. 31 to cost fares for its absolutely driverless robotaxi rides in Abu Dhabi, and claimed that eradicating human employees from the vehicles would permit it to make a revenue on every car.
That places Pony.ai furthest from profitability among the many three main Chinese language robotaxi operators. Its CFO Leo Haojun Wang informed The Wall Avenue Journal in mid-September that the corporate aimed to make a revenue on every automotive by the top of this 12 months or early subsequent 12 months.

Pony.ai plans to launch a totally autonomous industrial robotaxi enterprise in Dubai in 2026, after receiving a testing allow in late September. The corporate plans to roll out in Europe within the coming months and has additionally outlined an growth into Singapore.
Pony.ai and WeRide are set to launch quarterly earnings early subsequent week.
“Presently, corporations like Waymo, Baidu, WeRide and Pony.ai are main when it comes to fleet dimension, which positions them advantageously within the race for profitability,” stated Yuqian Ding, head of China Autos Analysis at HSBC.
Scale and security
Fleet dimension is changing into a aggressive marker. Pony.ai reportedly stated it plans to launch 1,000 robotaxis within the Center East by 2028, whereas WeRide goals to function a fleet of 1,000 robotaxis within the area by the top of subsequent 12 months.
Niu stated Apollo Go operates round 100 robotaxis in Abu Dhabi and Dubai, and plans to double its car fleet within the subsequent few months.
“Apollo Go has had a head begin with considerably extra take a look at rides than the opposite two,” Kai Wang, Asia fairness market strategist at Morningstar, stated in an e mail. “The extra testing and information you’ll be able to acquire from journeys taken, the extra doubtless the AI sensors are capable of acknowledge the objects on the highway, which suggests higher security as nicely.”
He cautioned that regardless of some preliminary progress, the robotaxi race stays unsure as “nobody has really had mass adoption for his or her autos.”
Protection stays restricted. Even in China, robotaxis are solely allowed to function in chosen zones, although Pony.ai just lately grew to become the primary to win regulatory approval to function its robotaxis throughout all of Shenzhen, dubbed China’s Silicon Valley. In Beijing, self-driving taxis are principally restricted to a suburb referred to as Yizhuang.
Anecdotally, CNBC assessments have discovered Pony.ai supplied a smoother trip than Apollo Go, which was liable to laborious braking.
As for security — which is vital for regulatory approval — not one of the six operators has reported fatalities or main accidents attributable to the robotaxis up to now. However Apollo Go and Waymo have begun promoting low airbag deployment charges.
Even when that is not sufficient to persuade regulators worldwide, Beijing is predicted to ramp up assist at house.
HSBC’s Ding predicts the variety of robotaxis on China’s roads may multiply from a couple of thousand to tens of hundreds between the top of this 12 months and 2026, a shift that will give operators extra proof that their mannequin works.