Owing to the continuing federal authorities shutdown, numerous key US financial information releases are at the moment unavailable. The Federal Reserve, the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the Bureau of Financial Evaluation, and the Census Bureau have suspended or delayed varied updates. Consequently, the Enterprise Situations Month-to-month indicators will likely be unavailable till regular information publication resumes.
Dialogue, September–October 2025
Though the September 2025 CPI will likely be launched on October 24, the exigencies of publishing deadlines require the Enterprise Situations Month-to-month to be issued earlier than its launch. However, the next feedback are germane to the continuing macroeconomic dialogue.
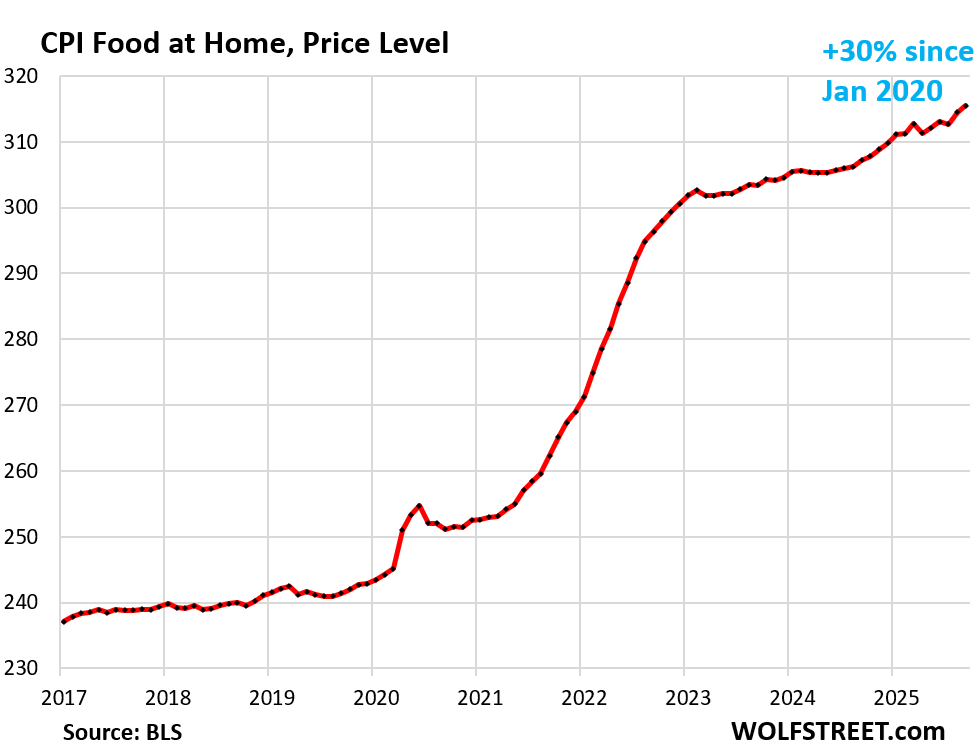
Amid the continuing authorities shutdown, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) delayed the September CPI report from October 15 to October 24 and faces a larger problem for October’s CPI, which can doubtless embody fewer collected costs and decrease statistical accuracy. The shutdown has halted most discipline operations, that means roughly 60 p.c of CPI value quotes (these gathered by in-person and phone surveys) will likely be lacking for a lot of October, whereas 40 p.c gathered by way of on-line and company information may be retroactively added later. Ought to the federal government reopen over the last week of October, as a lot as one-third of value information might nonetheless be lacking, with the housing survey — the most important CPI part, representing about one-third of whole weight — particularly affected, doubtlessly dropping two-thirds of its regular sampling. This can widen the 95 p.c confidence interval for headline CPI, with resultant errors lingering into spring because the affected housing panel stays within the pattern by way of Might 2026.
Broader distortions might additionally persist throughout classes like airfares, lodges, and regionally staggered city surveys, as a number of depend on bimonthly information assortment and imputed pricing. Though various datasets akin to Truflation and the Adobe Digital Value Index will present interim steerage, they’re methodologically inconsistent with CPI and threat including noise. Bloomberg experiences that high-frequency monitoring of thousands and thousands of costs signifies that tariff-sensitive items have just lately seen declines, whereas holiday-related classes like toys present remoted will increase. Taken collectively, the proof means that the September CPI launch will likely be reasonable sufficient to strengthen expectations of an October charge lower, although October’s studying is more likely to be statistically noisier than typical.
With official BLS experiences suspended amid the federal government shutdown, the nationwide employment image should be pieced collectively from state information and personal sources. Estimates counsel that preliminary jobless claims fell to about 215,000 within the week ended October 11, indicating layoffs stay traditionally low regardless of a short lived spike in unemployment claims from furloughed federal employees underneath the Unemployment Compensation for Federal Staff (UCFE) program. Continued claims held close to 1.9 million, pointing to regular labor-market absorption at the same time as a number of states did not report. In the meantime, the ADP Analysis Institute’s September estimate of a 32,000 drop in non-public payrolls doubtless overstates weak point attributable to methodological quirks tied to its re-benchmarking in opposition to incomplete Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) information and timing variations with BLS procedures. Adjusting for these components, true web hiring is probably going close to 55,000, supported by various information from Homebase and Revelio Labs exhibiting private-sector job positive factors between 60,000 and 150,000. Taken collectively, accessible indicators painting a labor market that continues to be resilient however is exhibiting gentle cooling on the margins; an image far much less dire than ADP’s headline determine implies.
Though September’s information had been launched underneath the shadow of a authorities shutdown, the accessible indicators counsel a transparent cooling in US financial exercise throughout each the providers and items sectors. The huge providers economic system successfully stalled, with the ISM Companies Index falling to a impartial 50.0 as enterprise exercise contracted for the primary time since 2020 and new orders flattened. Employment continued to shrink for a fourth month, constrained by cautious hiring and chronic labor mismatches, whereas provider deliveries slowed extra from trade-policy disruptions than from real demand stress. Inflation in providers remained cussed, with costs paid rising to close three-year highs at the same time as demand weakened — a troubling combine for policymakers already balancing slower progress and sticky prices.
On the products manufacturing aspect, manufacturing unit exercise remained in contraction for a seventh straight month, with the ISM Manufacturing PMI inching as much as 49.1 however nonetheless signaling decline. Output and employment improved barely, but new orders and backlogs fell once more, inventories had been drawn down, and tariff-related frictions stored confidence low. Enter-price progress eased for a 3rd consecutive month, suggesting fading pipeline inflation at the same time as commerce uncertainty, excessive borrowing prices, and weak international demand weighed on output. Taken collectively, the info depict an economic system dropping momentum on each fronts: manufacturing continues to battle for traction whereas providers — the same old ballast — has slowed to a crawl, leaving progress more and more fragile heading into the ultimate quarter of the 12 months.
Client confidence softened in September and early October as Individuals grew much less optimistic about inflation and the labor market. The College of Michigan sentiment index slipped to 55.0, its lowest in 5 months, as households reported weaker revenue expectations and the next perceived threat of job loss. Practically two-thirds of respondents anticipate inflation to outpace wage positive factors within the coming 12 months, whereas a couple of third foresee rising unemployment — virtually twice the share from a 12 months earlier. Shopping for situations for big-ticket gadgets worsened amid tariff-related value considerations, although decrease borrowing prices modestly improved views on residence and car purchases. Brief-term inflation expectations eased barely to 4.6%, whereas long-term expectations held at a still-elevated 3.7%, suggesting persistent nervousness about prices at the same time as spending continues.
Small-business optimism additionally slipped, with the Nationwide Federation of Unbiased Companies (NFIB) index falling to 98.8 in September, the bottom since June 2025 as homeowners grew extra cautious about gross sales, inventories, and inflation. Expectations for higher enterprise situations over the following six months dropped sharply, and concern over extra stockpiles reached a multi-decade excessive. But operational indicators had been steadier: hiring and capital-spending plans ticked up, and revenue tendencies improved modestly. Roughly a 3rd of corporations plan to lift costs to offset tariff and enter prices, whereas the NFIB’s uncertainty index jumped to its highest since February. Collectively, each shoppers and companies stay essentially resilient however more and more uneasy — sustaining exercise for now, but bracing for slower progress and policy-driven volatility forward.
At current, that confidence is barely marginally expressing itself in retail consumption, as a wave of high-frequency indicators factors to shoppers easing off the accelerator after a vigorous summer time of spending. Credit score- and debit-card information from Financial institution of America and Bloomberg Second Measure present a pullback in discretionary classes akin to furnishings, attire, and residential electronics, in keeping with a moderation following 4.1% annualized progress in retail exercise over the prior three months. Whereas middle- and higher-income households continued to spend modestly — helped by inventory market positive factors and lingering momentum from earlier within the 12 months — lower-income shoppers confirmed indicators of fatigue, constrained by slower wage progress and persistently excessive costs. The Federal Reserve’s Beige E book characterised retail exercise as having “inched down,” echoing private-sector experiences that counsel consumers are looking for extra reductions and delaying massive purchases. Nonetheless, Walmart and Wells Fargo reported regular spending patterns, suggesting no collapse — only a normalization. General, retail information painting a cooling however nonetheless sturdy client sector: regular sufficient to maintain progress, but more and more cautious as labor situations soften and households brace for the vacation season amid financial and coverage uncertainty.
Earlier than attending to an general evaluation — as far as one is feasible with out the core statistical releases — a phrase is warranted in regards to the authorities shutdown and its influence on the US economic system. Now coming into its fourth week, what was initially anticipated to be a brief standoff has develop into a drawn-out political spectacle that would simply stretch into November. Prediction markets akin to Kalshi now place its doubtless length close to 40 days, rivaling the 35-day report of 2018–19. The instant results, although actual, are largely restricted: a whole bunch of 1000’s of federal workers have missed paychecks, air journey has been strained by unpaid visitors controllers and TSA workers, and IRS, park, and diet packages have curtailed operations. A extensively broadcast estimate holds that every week of closure shaves 0.1 to 0.2 share factors from GDP, losses that will likely be partly recouped as soon as again pay is issued — however doubtlessly much less so if the administration follows by way of on proposed federal layoffs. Opinion polls present almost half of American respondents cite “the potential hit to the economic system” as their chief concern, though there’s a threat that political brinkmanship might start to dent client and enterprise sentiment if it drags deeper into the fourth quarter.
That stated, the financial influence of shutdowns has traditionally been extra theatrical than catastrophic. No US recession has ever been triggered by one, and markets have proven little panic amid the present deadlock. The larger threat lies not within the misplaced output however within the erosion of confidence and the cumulative impact of delayed information, stalled packages, and political dysfunction. One might argue that momentary discomfort is a value price paying if it spurs a severe reckoning with unsustainable deficits and debt — however historical past provides little encouragement that such episodes result in lasting fiscal reform. Extra typically, shutdowns finish not with structural options however with one other momentary repair, leaving the underlying budgetary pressures intact and public endurance thinner.
Within the broadest sense, US financial exercise in September and early October was little modified, with progress uneven and sentiment subdued throughout areas. The Federal Reserve’s newest Beige E book describes an economic system holding regular however dropping momentum on the margins: client spending edged decrease, employment ranges had been broadly steady, and value pressures remained persistent. Tariffs continued to push up enter prices, although companies differed in whether or not they absorbed or handed these will increase on to prospects. A number of districts reported flat or modestly weaker exercise, whereas just a few noticed slight progress; most contacts described situations as tender however not collapsing. Labor markets, although looser, confirmed indicators of recalibration moderately than deterioration — some employers trimmed headcount by way of attrition, whereas others discovered hiring simpler as demand cooled. Persistent strains stay in hospitality, agriculture, and manufacturing, compounded by latest immigration coverage shifts and tariff uncertainty. With inflation nonetheless above goal and progress barely advancing, the Fed is anticipated to chop charges once more later this month to regular situations. The Enterprise Situations Month-to-month indicators will likely be up to date when the constituent information is offered. For now, the image that emerges is of an economic system that continues to be in delicate stability: not contracting, however slowing underneath the mixed weight of commerce frictions, coverage uncertainty, and eroding confidence from each shoppers and companies.
CAPITAL MARKETS PERFORMANCE